The Engineering Balance: Key Technologies Behind the Waterproof Air Permeable Membrane
2026-01-08
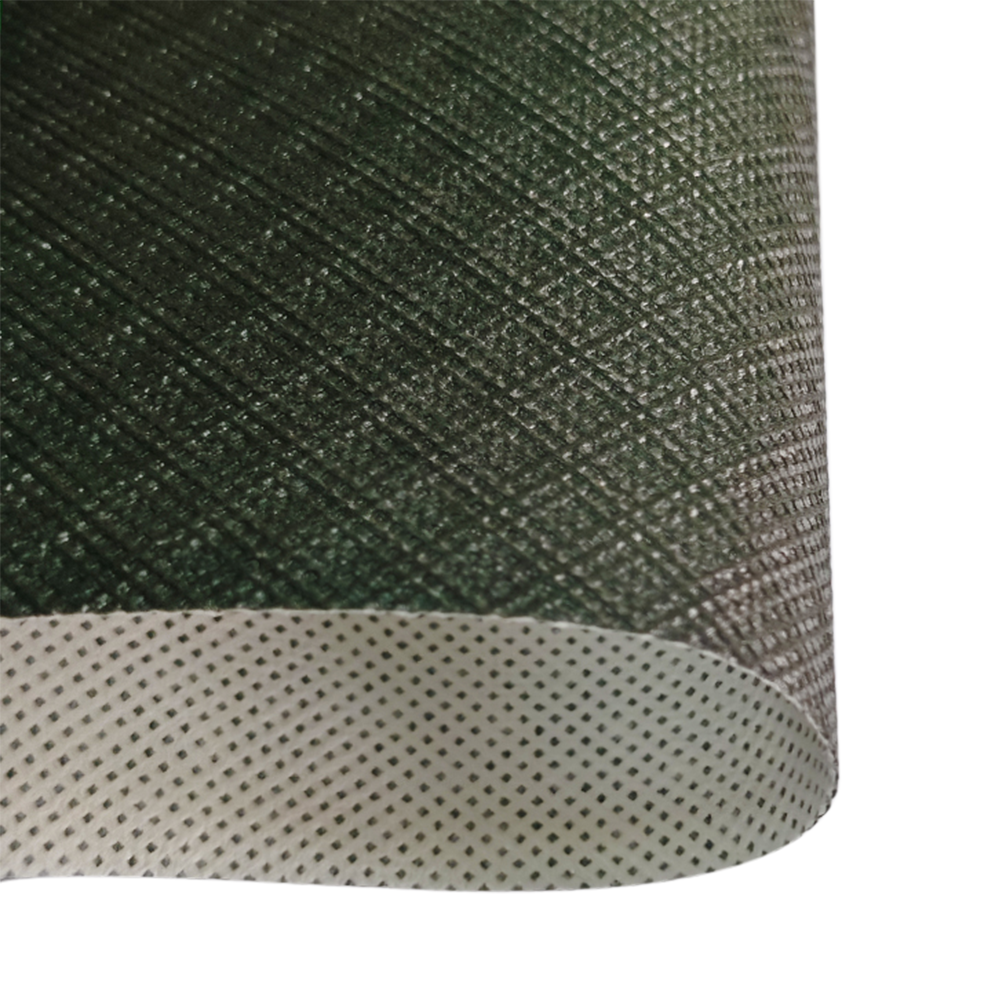
In the specialized sectors of building enclosures, medical protection, and agricultural infrastructure, the Waterproof Air Permeable Membrane serves as a critical functional barrier. The core challenge for engineers is managing the "breathability-waterproof paradox": creating a structure that prevents liquid water ingress while facilitating the diffusion of water vapor. Jiangsu Aotelong New Materials Co., Ltd. (also known as Zhongning New Materials) has addressed this through decades of R&D. Based in Yangzhou, we operate as a large-scale enterprise integrating the production of high permeability waterproof breathable membrane and vapor barrier membrane. Our commitment to quality is validated by US ICC-ES and UK BBA factory inspections, ensuring our composite materials meet the most rigorous international standards for durability and performance.
1. Microporous Architecture and Pore Size Distribution
The primary mechanism of a Waterproof Air Permeable Membrane relies on a microporous functional layer, typically made of functional polyolefin. The pore size must be significantly larger than a water vapor molecule (approx. 0.0004 microns) but much smaller than the smallest raindrop or water droplet (approx. 100 microns). According to the 2024 Global Technical Textiles Market Analysis by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the precision of pore size distribution is now the leading indicator of a membrane's service life, with advanced breathable roof membrane for timber frame construction requiring a "narrow-band" distribution to prevent pore clogging over time. By narrowing the pore distribution, we can increase the WVP (Water Vapor Permeability) of waterproof breathable membrane without compromising its hydrostatic head (water resistance).
Source: IFC - International Finance Corporation: 2024 Technical Textiles Industry Report
Technical Comparison: Pore Size vs. Functional Efficiency
While standard membranes may have inconsistent pore sizes that lead to localized leakage, high-performance variants utilize uniform micropores to ensure reliable vapor exit and liquid rejection.
| Performance Characteristic | Standard Low-Permeability Grade | High permeability waterproof breathable membrane |
| Average Pore Size | 0.5 - 2.0 Microns | 0.1 - 0.3 Microns (Optimized) |
| Hydrostatic Pressure | > 1000 mm | > 5000 mm |
| Vapor Transmission | Low to Moderate | High (> 2500 ) |
| Application Suitability | General packaging/Industrial | High-end building/Medical (SMS/SMMS) |
2. Non-Woven Substrate Engineering: PP Spunbond and SMS Layers
The functional membrane is inherently fragile and requires a structural carrier. The choice of non-woven fabric, such as PP spunbond non-woven fabric for membrane base, is vital for mechanical strength and UV protection. According to the 2025 Strategic Standards released by the European Disposables and Nonwovens Association (EDANA), the bond strength between the functional film and the non-woven substrate must now withstand higher mechanical stresses to prevent delamination in extreme weather. At Jiangsu Aotelong, we utilize advanced thermal bonding and ultrasonic lamination to combine the functional film with PP Spunbond, SMS, or SMMMS layers. This ensures that a UV resistant waterproof breathable membrane for walls maintains its structural integrity even during the prolonged exposure phases of a construction project.
Source: EDANA - 2025 Quality Standards for Nonwoven Composites
Technical Comparison: Substrate Material Impact
Single-layer spunbond provides basic protection, whereas multi-layer SMS and SMMMS structures provide superior liquid barriers and tensile strength for medical and high-stress building applications.
| Substrate Technology | Tensile Strength (MD/CD) | Air Permeability Impact |
| Standard PP Spunbond | Moderate | Minimal Resistance |
| SMS (Spunbond-Meltblown-Spunbond) | High | Moderate Filtering Effect |
| SMMMS Composite | Ultra-High | High Barrier / Controlled Permeability |
3. Balancing Diffusion and Hydrostatic Head
Achieving the perfect balance requires managing the surface energy of the materials. To be effectively "waterproof," the membrane surface must be hydrophobic (water-repelling). However, for a vapor barrier membrane, the goal is to prevent moisture movement entirely, which is the opposite of a breathable membrane. This distinction is critical for engineers designing building envelopes in different climates. Jiangsu Aotelong provides both high and low permeability options, ensuring that whether it is an agricultural greenhouse or a surgical gown, the WVP (Water Vapor Permeability) of waterproof breathable membrane is tuned to the specific environmental humidity and temperature gradients.
- Hydrophobic Coatings: Applied to the outer non-woven layer to facilitate water "beading" and runoff.
- Anti-Aging Additives: Essential for UV resistant waterproof breathable membrane for walls to prevent polymer degradation.
- Reflective Lamination: Optional reflective insulation layers can be added to reduce thermal transfer in building enclosures.
- Certifications: Compliance with CE, BBA, and ICC-ES ensures the product meets global building codes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between high and low permeability membranes?
A high permeability waterproof breathable membrane allows a large volume of water vapor to pass through (ideal for venting internal moisture), whereas low-permeability or vapor barrier membrane types are designed to restrict vapor movement to protect insulation from condensation.
2. Can the membrane be used as a permanent exterior finish?
While products like our UV resistant waterproof breathable membrane for walls offer excellent weather protection, they are designed as underlayments. They should be covered by a primary cladding or roofing material within the specified UV exposure window (usually 3-4 months).
3. Why is pore size distribution important for timber frames?
In a breathable roof membrane for timber frame, uniform pore distribution prevents the "tent effect," where pressure or contact with the timber might otherwise force water through the membrane.
4. How does the PP Spunbond layer affect the overall quality?
The PP spunbond non-woven fabric for membrane base provides the necessary tear resistance and tensile strength. Without a high-quality substrate, the functional film would tear during installation or under wind loads.
5. Is your membrane suitable for medical applications?
Yes. Jiangsu Aotelong produces SMS, SMMS, and SMMMS composite non-woven fabrics that are used in surgical gowns and protective clothing, offering high microbial barriers while maintaining wearer comfort through breathability.


 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский España
España عرب .
عرب .